As we approach 2025, the landscape of cyber insurance faces multiple challenges, which need to be addressed as we move forward. In addition, security breaches are becoming more common and costlier. The business landscape is evolving rapidly, influenced by increasing cyber threats, advanced technology, and regulatory changes. Since cyber threats have become common among organizations, the cyber insurance market has witnessed rapid growth and significant evolution influenced by the increasing frequency and severity of cyberattacks. The growing recognition of cyber risks by businesses also influenced the growth and evolution of the cyber insurance market in the recent past. In addition to this, the cyber insurance market has experienced significant growth and transformation as it adapts to an evolving cyber threat landscape.
As the frequency of cyberattacks continues to rise and the risks associated with them grow, the requirement for cyber insurance will grow. These rising cyberattack incidents have created a significant impact on awareness of cyber risks and built regulatory pressures, which are leading to the growth of cyber insurance and the market worldwide. Further, the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, particularly those utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies, also contributes to the growth cycle of cyber insurance.
Overview of Cyber Insurance
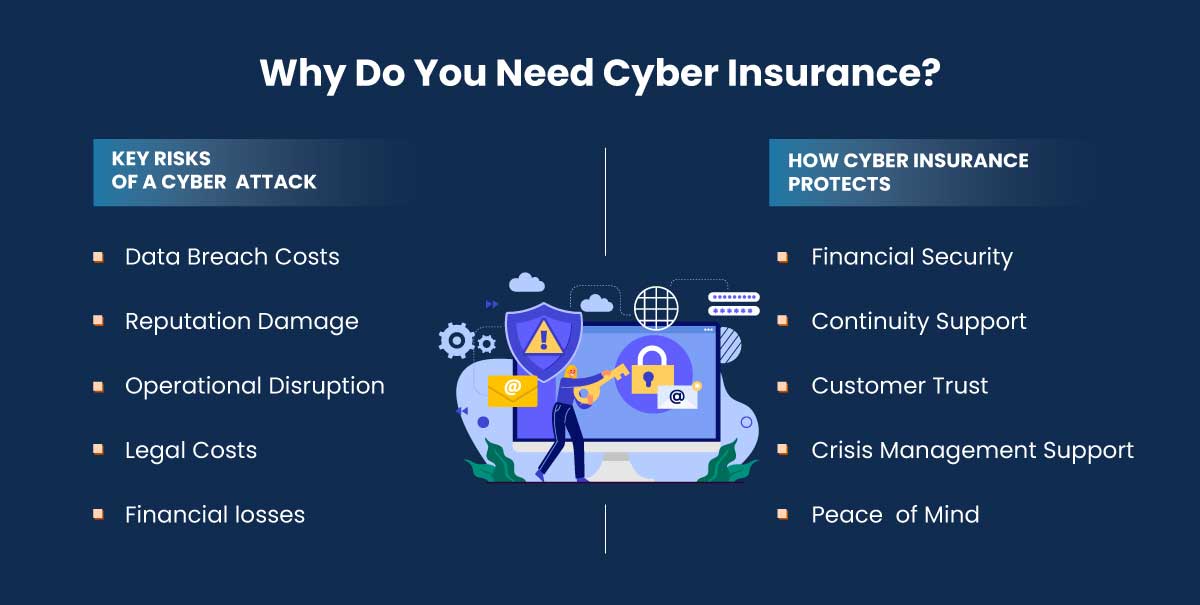
Cyber insurance, also known as cybersecurity insurance is a specialized form of insurance coverage designed to protect businesses operating or handling sensitive data on the internet. This insurance coverage protects businesses from any financial losses resulting from cyber incidents such as ransomware attacks, data breaches, hacking, phishing, data theft, and various other cyber risks.
Cyber insurance provides financial support for the costs associated with these incidents and services to help mitigate risks and manage the aftermath. As businesses increasingly rely on digital technologies and the frequency and sophistication of cyber threats continue to rise, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats. These increasing trends in cyberattacks contribute to the importance of cyber insurance.
Recommended: Proactive Cybersecurity: Key Steps for IT Leaders to Defend Against Attacks in 2025
Key Features of Cyber Insurance
1. Common Coverage Areas
Cyber insurance can cover a wide range of incidents and expenses. The coverage areas are broadly categorized into first-party coverage and third-party coverage.
Here are the common coverage areas included in most cyber insurance policies:
- Costs for forensic investigations and data recovery.
- Legal fees associated with compliance and litigation.
- Public relations efforts to manage reputational damage.
- Business interruption losses due to system outages.
- Notification costs for affected individuals in case of a data breach.
In the digital age, not having cyber insurance can cause severe consequences for businesses and expose them to severe risks such as breach expenses, ransomware costs, revenue loss, trust erosion, data loss, high recovery costs, and operational disruptions.
2. Coverage Types
The myth around cyber insurance is that only big organizations need cyber insurance; however, any business regardless of size needs cyber insurance if they are operating or handling sensitive data using the internet. Cyber insurance policies typically include two main types of coverage:
First-Party Coverage: This cyber insurance protects the insured organization against direct losses in cyber incidents and costs associated with data recovery, business interruption, breach costs, and reputational damage.
Third-Party Coverage: This coverage addresses liabilities arising from claims made by affected parties due to a cyber incident. These claims include legal defense costs and settlements resulting from lawsuits related to data breaches or privacy violations.
Recommended: 5 Key Predictions for the Future of Cloud from AWS re:Invent 2024
Key Trends in Cyber Insurance
1. Growth in Premiums
As cyberattacks continue to rise, there is a growing emphasis on ransomware-specific policies. This trend is contributing to the rise of premiums covered by the insurer to cover the rising costs of claims. High-risk target sectors such as finance, e-commerce, healthcare, and critical infrastructure are witnessing the impact of these trends. The growth in premiums is driven by rising awareness of cyberattack risks such as ransomware and data breaches. Moreover, the increasing frequency of cyberattacks reflects the urgent need for organizations to bolster their defenses against their pervasive threats. As the frequency of cyberattacks rises, this trend may impact businesses with weak cybersecurity measures.
2. AI-Driven Risk Assessment
In 2025, the rise of AI will contribute a significant amount of innovation in cybersecurity measures and cyber insurance. It is projected that by 2025, insurers will shift from static annual assessments to AI-driven and real-time evaluations of a company’s cybersecurity posture. The shift will allow cyber insurers to monitor a wide range of ongoing security practices and make adjustments in premiums based on actual risk levels rather than historical static data. Moreover, companies adopting advanced security measures will likely benefit from lower premiums.
3. Tighter Policy Requirements
With the rise in cyberattack frequency and the sophisticated techniques from cyber criminals, cyber insurers are tightening their coverage requirements with a focus on advanced and specific security systems such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Managed Detection and Response (MDR). A tighter policy with a focus on specific security systems will be a crucial change in 2025. As businesses introduce these security systems in operations, it will significantly reduce their risk profile and potentially lower their insurance costs.
4. Focus on Supply Chain Security
The increasing focus on supply chain security is significantly influencing the landscape of cyber insurance worldwide. As supply chain hacks increase in frequency, the Insurers will stress the importance of third-party contractors with strong security measures. To be eligible for cyber insurance coverage, organizations will be required to prove that their partners follow strict cybersecurity guidelines as well.
5. Regulatory Compliance Pressures
As businesses move with the digitalization of their operations and data, stricter regulatory frameworks are expected to make a big impact in 2025. Regulatory frameworks such as the EU IoT Regulation and SEC Cybersecurity Disclosure Rules will require businesses to invest in compliance measures, which may impact their eligibility for certain insurance policies. This trend is likely to influence insurers to adjust their offerings based on compliance levels.
Recommended: Predictions Insights 2025: 5 Most Advanced Types of Cyberattacks Every CISO Should Know
Risks Associated with Cyber Insurance
1. Evolving Threat Landscape
The cyber threat landscape is rapidly evolving with the rise of sophisticated attacks, particularly those driven by AI. These sophisticated cyberattacks pose significant risks to insurers. In addition, advanced tools like Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and automated campaigns such as phishing emails contribute to the rise of cyberattacks, leading to increased claims and potential losses for insurers.
2. Increased Claims Frequency and Severity
The cost of cyber insurance has been increasing significantly with the frequency of cyberattacks, making it challenging for small and medium-sized businesses to afford adequate coverage. Moreover, increased cyber claims put pressure on financial and professional lines. In the recent decade, the frequency of large cyber claims has risen sharply, and it is likely to increase further as the cyberattacks get more sophisticated.
As insurance claims grow in size and frequency, insurers face pressure on profitability and may need to adjust their pricing strategies to adjust their profitability.
3. Lower Retention Rates
The influx of new players and the market conditions have intensified competition, leading to lower retention rates and premiums. However, in the short run, this might help customers, but if not handled wisely, it might put pressure on insurers’ profit margins.
4. Systemic Risk Management Challenges
With growing concerns about cyber threats, it is necessary for cyber insurers to navigate complex systemic risks associated with large-scale incidents that can impact multiple clients simultaneously. Coordinated ransomware attacks are such events that present unique challenges in risk modeling and claims management.
5. Potential for Increased Ransomware Attacks
The availability of cyber insurance in the event of cyberattacks has raised an unexpected concern that it may inadvertently encourage cyber incidents such as ransomware attacks. This trend is likely to give a boost to the increased ransom demands from hackers as businesses become more comfortable paying ransom due to insurance coverage.
Who Needs Cyber Insurance?
As businesses transform and increasingly rely on digital operations, the risks associated with cyber threats are on the rise, making strict security measures a crucial component of cyber insurance for low premiums. Cyber insurance is not limited to safeguarding businesses from financial instability and providing financial protection but it also contributes in enhancing businesses resilience in the face of potential attacks.
As businesses increasingly adopt digitalization, the frequency of cyberattacks is rising, and so is the average cost of a data breach. These trends are influencing and shaping cyber insurance and risk management strategies for businesses.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach report, “83% of organizations have had more than one data breach, and the average breach costs USD 4.35 million.” This trend shows why cyber insurance is an essential component of risk management strategies for businesses of all sizes.
Recommended: Is Your Healthcare Data Safe? Discover the Top AI Cybersecurity Tools Protecting the Industry
Cyber insurance should be considered by businesses that handle sensitive consumer information or participate in online operations. This covers companies across a range of industries, including technology, healthcare, finance, and e-commerce, critical infrastructure. Businesses or organizations that store payment information, proprietary data, or Personally Identifiable Information (PII) should prioritize securing the right coverage. In the event of a cyberattack, cyber insurance can reduce the financial effect of data breaches.
Conclusion
The cyber insurance market is growing rapidly in response to the increasing cyber risk landscape. In the wake of growing cyber threats, cyber insurance is an important part of contemporary company risk management techniques. As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must the strategies employed by both businesses seeking coverage and insurers providing it.
The trends for 2025 indicate a shift towards more dynamic risk assessments, stricter policy requirements, and an emphasis on compliance with emerging regulations. The risk associated with cyber insurance indicates a shift towards recognizing and addressing systemic risks within the cyber landscape.
In an increasingly competitive cyber insurance market, organizations should adopt enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect themselves and to secure favorable terms. Insurers must adapt to opportunities and challenges shaped by technological advancements and an increasingly complex threat landscape by enhancing their understanding of emerging risks, particularly those driven by AI while fostering stronger cybersecurity practices among their clients.
In the coming years, the interplay between the evolving nature of cyber risks and the increasing need for coverage will influence how the sector changes.
To share your insights, please write to us at news@intentamplify.com