Artificial intelligence (AI) has moved from being a promising experiment in cybersecurity to a board-level priority. Enterprises today face adversaries who leverage automation, machine learning, and even generative AI to scale attacks at unprecedented speed.
In response, security operations centers (SOCs) are pressured to modernize, balancing automation with human expertise, integrating AI across architectures, and aligning with Zero Trust principles.
This blog explores the AI security trends shaping enterprise defense strategies, focusing on threat detection and SOC automation. It blends strategic insight with technical depth, designed for CIOs, CISOs, and security leaders navigating the next wave of enterprise security architecture.
Current AI-Driven Threat Landscape
The threat landscape has shifted dramatically in the past 24 months.
AI-Powered Attacks
Generative AI is increasingly weaponized to create polymorphic phishing campaigns and malware variants that evade traditional detection.
In April 2025, SecurityWeek revealed that 76% of all phishing assaults had at least one polymorphic element and that phishing emails had risen by 17% in February 2025 compared to the preceding six months.
Subject lines, sender display names, and content are all randomized in polymorphic phishing, making detection much more difficult.
Speed and Scale
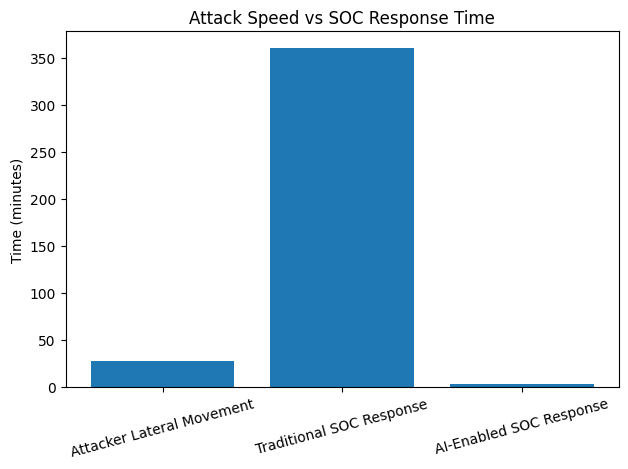
Attackers can move laterally quickly, often in less than 30 minutes, which drastically reduces the time it takes for defenders to react.
Attackers can move laterally in as little as 27 minutes (average 48 minutes). According to ReliaQuest’s 2025 Annual Threat Report, AI-enabled SOCs can contain attacks in roughly 3 minutes as opposed to 6 hours for conventional approachttps://reliaquest.com/blog/insights-from-reliaquests-2025-annual-threat-report/hes.
The necessity for AI-driven security to keep up with the attacker pace is highlighted by this data.
Supply Chain Risks
Particularly in industries like healthcare, banking, and defense, AI models create supply chain vulnerabilities like data poisoning, model theft, and malicious integrations.
Increase in covert attacks, including data poisoning and hostile models that target pre-trained models with limited transparency, are highlighted in Google guidance on AI supply chain security 2025 analysis. Threats to large providers like OpenAI and occurrences like the Hugging Face malware increase risks.
The insights from the blog state, “The ecosystem for storing, changing, and retrieving datasets is less mature than that for code management, but it is required at Google for AI. Tamper-proof provenance can help developers verify the identity of the model producer and confirm the model’s authenticity.”
Cloud-Native Threats
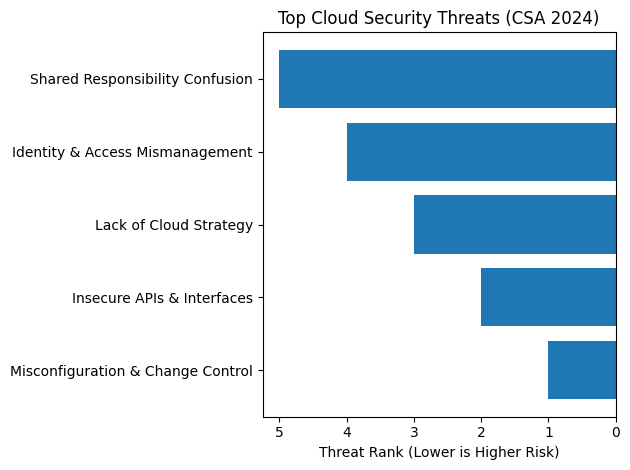
As businesses migrate workloads, misconfigurations and insufficient change controls become more significant cloud risks than identity and access management problems.
Misconfiguration/change control is now ranked #1 in the Cloud Security Alliance’s 2024 Top Threats to Cloud Computing study, up from third in 2022. Key issues include insecure interfaces, APIs, and a lack of a cloud strategy.
Sean Heide, technical research director for the CSA, shared, “Given the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, it’s difficult for companies to stay ahead of the curve and mitigate their financial and reputational risks. By bringing attention to those threats, vulnerabilities, and risks that are top-of-mind across the industry, organizations can better focus their resources.”
Reports from ENISA and Gartner highlight that AI-driven threats are now systemic, requiring enterprises to rethink detection and response capabilities. SOCs must evolve from reactive monitoring to proactive, AI-augmented defense.
Why SOC Modernization Matters to Company Leadership
Modernizing the security operations center isn’t just another IT upgrade; it’s got the attention of the whole leadership team now. These days, cyberattacks don’t just mess with your tech. They hit revenue, shake customer trust, and put you at risk with regulators.
When something goes wrong, it’s not just the IT folks scrambling. Everyone, from legal to marketing, experiences it. Regulators are only turning up the heat.
With standards like NIST CSF 2.0 and Europe’s NIS2 Directive, companies need stronger defenses and a real plan for automation.
Then there’s the talent shortage. Right now, the world is short of more than 3.5 million skilled cybersecurity pros. If you’re hoping to keep up without burning out your team, automation isn’t just helpful, it’s essential.
Accountability is another big one. When a breach happens, the board and CEO don’t get to hide behind IT. They’ve got to answer for it. SOC performance isn’t just a tech issue anymore—it’s a core part of running the company responsibly.
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Old-school, signature-based security tools can’t keep pace with attackers using AI. So, companies are switching to smarter defenses.
Behavioral analytics learns what “normal” looks like for your people and systems, then flags anything weird. Anomaly detection powered by machine learning spots strange patterns in network traffic or devices. Predictive intelligence takes things even further, using AI to figure out where the next attack could come from before it even starts.
How ML, UEBA, XDR, and AI Correlation Engines Fit In
Machine learning lets your security adapt, fast. It learns new attack tactics as soon as they show up. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) digs deep into behavior data to spot insider threats or compromised accounts.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR security) pulls together alerts from endpoints, networks, and the cloud so security teams get the full picture. AI correlation engines connect all these dots, cutting through the flood of alerts so teams can focus on what’s real.
Modernizing the SOC isn’t just about chasing the latest tech. It’s about protecting the business, making leadership accountable, and staying one step ahead in a world where cyber threats never quit.
Limitations and Risks of Over-Automation
While automation enhances speed, risks include:
False positives: Over-reliance on ML can overwhelm analysts with noise.
Adversarial ML: Attackers can manipulate models to evade detection.
Context gaps: AI may misinterpret business-critical anomalies as benign.
Enterprises must balance automation with human-in-the-loop oversight to ensure accuracy and accountability.
SOC Automation for Enterprises
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms are central to SOC modernization:
Playbook automation: Automates repetitive tasks like phishing triage.
Autonomous response: AI-driven containment actions (e.g., isolating endpoints).
Analyst augmentation: AI copilots assist analysts with contextual recommendations.
Human-in-the-Loop Models
The most effective SOCs adopt human-in-the-loop frameworks:
- AI handles repetitive triage.
- Analysts validate high-risk actions.
- Governance ensures accountability for automated decisions.
Metrics That Matter: MTTR, False Positives, Alert Fatigue
Executives track SOC performance through:
Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): Reduced via automation.
False positive rates: Critical to avoid wasted analyst time.
Alert fatigue: Balanced by AI-driven prioritization.
Enterprise Security Architecture in the AI Era
AI is embedded across the enterprise stack:
Identity security: Continuous authentication and risk-based access.
Network security: AI-driven traffic analysis for east-west visibility.
Cloud security: Automated misconfiguration detection and compliance monitoring.
Endpoint security: Behavioral detection of ransomware and advanced malware.
Reference Architectures for Large Enterprises
Enterprises adopt layered architectures:
- AI-enhanced SIEM + XDR for detection.
- SOAR for orchestration.
- Zero Trust as the guiding principle.
Alignment with Zero Trust Principles
AI strengthens Zero Trust by:
- Enforcing continuous verification.
- Automating micro-segmentation.
- Detecting anomalous lateral movement.
Cybersecurity Trends Optimized for Zero-Click Audiences
Zero-click audiences consume insights without deep engagement, and executives want instant clarity:
Executive summaries: One-page overviews.
Insight blocks: Highlight key metrics and risks.
Data-led conclusions: Charts and benchmarks for quick decision-making.
How AI Security Vendors Are Adapting
Vendors now deliver:
- Dashboard-driven insights.
- Automated executive reports.
- AI-generated summaries tailored for board consumption.
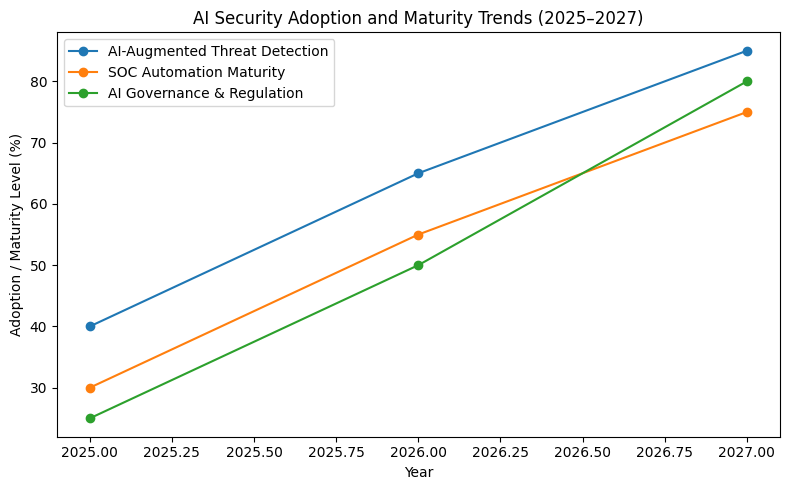
Top Cybersecurity Trends and Forecasts (2025–2027)
Regulatory frameworks are catching up, mandating transparency in AI use, while industry-specific models emerge to address vertical risks.
These trends highlight both the urgency and opportunity: enterprises that modernize now will be positioned to outpace adversaries and meet evolving compliance demands.
1. AI-Augmented Threat Detection Becomes Standard
XDR platforms integrate AI correlation engines, reducing false positives. Vendors like Palo Alto Networks, Microsoft, and CrowdStrike lead adoption.
2. SOC Automation Shifts to Autonomous Response
SOAR platforms evolve into autonomous SOCs, capable of isolating threats without analyst intervention. Splunk and IBM Security are investing heavily.
3. Cloud-Native AI Security Platforms Dominate
Cloud providers embed AI-driven detection into native services. AWS GuardDuty, Azure Sentinel, and Google Chronicle expand enterprise adoption.
4. AI Governance Emerges as a Compliance Requirement
Regulators mandate transparency in AI-driven security decisions. NIST and ENISA publish frameworks for responsible AI use.
5. Industry-Specific AI Security Models
Vendors develop vertical-specific AI models for healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, addressing unique threat vectors.
Top Industry Use Cases
These examples highlight how AI-driven defense strategies are being applied in real-world contexts, bridging compliance, operational continuity, and cyber risk reduction.
Financial Services
AI detects insider trading risks, automates fraud detection, and ensures compliance with Basel III and PCI DSS.
Healthcare
AI secures patient data, detects ransomware targeting hospitals, and supports HIPAA compliance.
Microsoft Threat Intelligence released research in late 2024 that highlighted the rising risk of ransomware in the healthcare industry.
“Healthcare organizations are an increasingly attractive target for threat actors. Ransomware continues to be among the most common and impactful cyberthreats targeting organizations,” Sherrod DeGrippo, Director of Threat Intelligence Strategy, shared.
Manufacturing and Critical Infrastructure
AI-driven anomaly detection protects OT environments, preventing downtime in industrial control systems.
Retail and Digital Commerce
AI combats payment fraud, secures e-commerce platforms, and protects customer identity data.
Government and Public Sector
AI enhances national cyber defense, secures citizen data, and supports compliance with evolving regulations.
Conclusion
Threat detection is entering a new phase. One where speed, scale, and intelligence define defensive advantage. As adversaries increasingly rely on automation and AI to execute attacks, security operations centers must evolve beyond reactive monitoring into continuously adaptive, AI-augmented defense environments.
SOC automation is no longer about efficiency alone. It is about resilience, accountability, and the ability to contain risk at machine speed while preserving human oversight. Enterprises that embed AI across their security architecture.
From detection and response to identity, cloud, and network controls. They are better positioned to reduce dwell time, manage alert fatigue, and align security outcomes with business objectives.
Effective adoption requires disciplined governance, transparent decision-making, and a human-in-the-loop approach that balances automation with expert judgment.
When anchored in Zero Trust Principles and supported by robust operating models, AI becomes a force multiplier rather than a source of new risk.
Reflect on how your current data practices stand up to the “Take Control of Your Data” ethos and identify one small change you can make today.
FAQs
1. How does AI security reduce SOC costs?
By automating repetitive tasks, AI reduces analyst workload, lowering operational costs while improving efficiency.
2. Can AI fully replace human analysts?
No. AI augments analysts but cannot replace human judgment, especially in complex, context-driven decisions.
3. What metrics should boards track for SOC performance?
MTTR, false positive rates, and incident containment times are critical indicators.
4. How does AI align with Zero Trust?
AI enforces continuous verification, detects anomalies, and automates segmentation, strengthening Zero Trust architectures.
5. What are the biggest risks of AI in security?
Adversarial ML, over-automation, and governance gaps pose significant risks if not managed properly.
To participate in upcoming interviews, please reach out to our CyberTech Media Room at info@intentamplify.com







