In 2024, organizations were exposed to advanced types of cyberattacks. With hundreds of new cyberattacks reported daily, CISOs have an overwhelming task to track, monitor, analyze, and report every incident, and plan how these attacks can be prevented. Moreover, cyber attackers, mostly involving individual hackers, political hacktivists, and state-sponsored gangs take advantage of new-age technologies such as Generative AI and CoPilot to launch sophisticated attacks. These attacks are based on incredible planning led by Big Data intelligence, and automation. According to Cisco’s recent Cyber Threat Trends report, threats are classified into these categories:
- Information stealers
- Trojans
- Ransomware
- Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)
- Botnet
- Dropper
- Backdoor
Backdoor attacks, for instance, follow a very unique methodology. Microsoft recently identified Tickler, a multistage backdoor vector, deployed by the Iranian state-sponsored attack group Peach Sandstorm. Tickler scrapped data from the internet and social media platforms like LinkedIn, to launch targets on vulnerable industries and institutions. According to the report, in April and May 2024, Microsoft detected Peach Sandstorm carrying out password spray attacks using Tickler against organizations in the defense, space, education, and government sectors in the US and Australia.
As we approach the New Year 2025, our CyberTech Insights analysts and reporters reviewed more than 150 reports, news, and digital resources to identify the 5 most advanced (and deadly) types of cyberattacks that can paralyze an organization.
Here’s our list.
- Watering Hole attacks
- Whale Phishing attacks or whaling
- AI Jailbreaking
- Remote Code Execution (RCE) attacks
- LLMjacking attacks
Let’s discuss in detail each of these advanced types of cyberattacks.
#1 Watering Hole Attack
If you have read Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book or visited the wildlife national parks in India or Africa, you can easily relate to a watering hole. In its natural existence, a watering hole is the perfect spot to ambush helpless prey who gather for drinking and cooling.
Let’s define a watering hole attack.
A watering hole attack is a sophisticated cyber threat that focuses on infiltrating groups of users by compromising websites they frequently visit. This term is derived from the behavior of predators that lie in wait at watering holes, ready to strike when their prey is most vulnerable. In the digital realm, attackers exploit niche websites, aiming to infect them with malware, which subsequently affects the visitors.
Watering hole attacks in the cybersecurity space are a decade-old concept, yet CISOs find new types of such attacks surfacing every day!
Watering Hole Attack tops our list of advanced types of cyberattacks every CISO should expect to grow more prominent in 2025. These attacks fall under the hybrid category of RAT and APTs. According to the UK’s National Cyber Security Center (NCSC), a watering hole attack exploits the vulnerabilities of an organization’s IT and networking system before affecting the visitors who use these platforms for different activities — paying bills, filling out forms, updating information, or checking latest updates.
Unlike phishing or spear-phishing attacks, which typically seek to extract sensitive information or install malware directly onto users’ devices, watering hole attacks work by infecting users’ computers and then enabling access to their corporate networks. This method allows cybercriminals to steal personal data, financial information, and intellectual property, and gain unauthorized access to sensitive corporate systems.
Although relatively uncommon, watering hole attacks maintain a high success rate due to their targeting of legitimate websites that cannot easily be blacklisted. Attackers often utilize zero-day exploits that evade detection by traditional antivirus software and scanners. As a result, these attacks represent a significant risk for organizations and individuals who may not adhere to established security protocols.
Recommendation:
- To combat this threat, organizations need to implement robust identification, tracking, and reporting measures.
- Treat all traffic as “untrusted”, until verified as trusted by a certified third-party security partner.
- Regular monitoring of user access patterns and website traffic can help detect unusual behavior.
- Additionally, employing advanced security solutions that focus on anomaly detection can assist in identifying potential watering hole sites before they compromise user systems.
- Timely reporting of suspicious activities can also facilitate a swift response, helping to mitigate the impact of such attacks.
- Implement Secure Web Gateways (SWGs) to enforce internet policies, filter malicious content, and protect against internal and external threats, especially with the increase of IoT and cloud applications.
#2 Whale Phishing Attacks
The Sysdig Threat Research Team (TRT) recently uncovered a widespread operation known as EMERALDWHALE, which targets exposed Git configurations and has led to the theft of over 15,000 cloud service credentials– most of these account credentials could be worth hundreds of dollars! CISOs should be careful of these attacks as they target the “whales” within an organization to steal vital data and sell them to the dark net operators. Hence, whale phishing or whaling attacks are on our list of the most advanced types of cyberattacks you should know in 2025.
According to Perception Point’s H1 2024 report on cybersecurity trends and insights, Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks grew by 42% in H1 2024, compared to H1 2023. Browser-based attacks made the bulk of phishing incidents in the same period, according to the report.
Is Whaling a big risk?
Whale phishing attacks target the “big fish” within an organization, primarily high-level executives such as those in the C-suite or other key decision-makers. These individuals often hold valuable information that can be highly sought after by cybercriminals including proprietary data and insights about the company’s operations. These attacks could aggravate into large-scale BEC attacks.
According to IBM, “Whale phishing, or whaling, is a type of phishing attack that targets high-level corporate officers with fraudulent emails, text messages, or phone calls. The messages are carefully written to manipulate the recipient into divulging sensitive corporate data and personal information or authorizing large payments to cybercriminals.”
When a high-profile target falls victim to a ransomware attack, they are more likely to pay the ransom to avoid the negative publicity that could harm their reputation and that of their organization. To mitigate the risk of whale phishing attacks, organizations should adopt the same preventive measures used against traditional phishing attempts. This includes meticulously reviewing emails, scrutinizing any attachments or links for suspicious elements, and being vigilant about unfamiliar URLs or parameters.
Identifying Whale Phishing Attacks
Whaling emails = hyper-personalized, to an extent where victims often self-doubt their own credibility. Such advanced attacks use social engineering tactics to build highly personalized contexts, including specific details about the recipient or their role in the organization, or family’s financial situation. In most cases, the attackers create a sense of urgency, prompting victims to act quickly without thorough scrutiny. Spoofed Email Addresses penetrate through the safety nets. Emails may appear to come from legitimate sources, often using similar domains to deceive recipients.
Red flags to identify when you receive an email:
- Unsolicited requests for sensitive information or financial transactions.
- Generic greetings instead of personalized salutations.
- Language that suggests immediate action is required.
Reporting and Tracking Whale Phishing
Reporting Mechanisms:
- Establish a clear reporting procedure for employees to flag suspicious emails. This could include forwarding the email to IT or a dedicated security team.
- Use centralized reporting tools that allow for the documentation of incidents for analysis and future reference.
Tracking Incidents:
- Maintain a log of reported phishing attempts to identify patterns or trends.
- Utilize security information and event management (SIEM) systems to analyze and correlate data from various sources to enhance threat detection.
Managing Whale Phishing Attacks with Advanced Types of Cyberattacks Readiness
Incident Response Plan:
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan against the advanced types of cyberattacks. The plan should outline procedures for responding to confirmed whaling attacks, including communication protocols and containment strategies.
- Train employees on the plan to ensure swift action when an attack is identified.
Security Awareness Training:
- Regularly conduct training sessions to educate employees about the characteristics of whale phishing attacks and the importance of vigilance. This should be done for all other advanced types of cyberattacks too.
- Use simulated phishing exercises to reinforce learning and enhance recognition of suspicious emails.
Recommended Steps to Prevent Whale Phishing Attacks
Implement Secure Web Gateways (SWGs): Utilize SWGs to enforce internet access policies and filter out malicious content, providing an additional layer of defense against phishing attacks.
Email Authentication Protocols: Deploy protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify the authenticity of incoming emails and reduce the chances of spoofed addresses reaching users.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for accessing sensitive accounts, adding an extra layer of security that makes it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Regular Software Updates: Keep all software and systems up to date with the latest security patches to minimize vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
Risk Assessment and Audits: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities within the organization and implement necessary controls.
Clear Communication Policies: Establish guidelines for communication that outline how sensitive information should be handled, including verification steps for financial transactions or data sharing.
Monitor for Anomalies: Use anomaly detection systems to identify unusual behavior, such as unexpected login attempts or irregular transactions, which may indicate a breach. Secops team should also study and evaluate the readiness against other advanced types of cyberattacks.
Security managers should evaluate the granular-level nuances of whale phishing attacks and implement robust identification, reporting, tracking, and management strategies. Organizations can significantly reduce their risk by establishing a culture of security awareness and vigilance among employees — an essential activity in creating a strong defense against these targeted cyber threats.
#3 AI Jailbreaking
We have two AI-enabled “as-a-service” cyberattacks on the list: LLMjacking and AI jailbreaking. Both attacks demonstrate the ‘darker’ side of AI’s use or abuse in the IT and security industry.
Let’s talk of AI jailbreaking.
AI jailbreaking, especially in conversational models like ChatGPT, is transforming the landscape of cyber threats. It underscores how new techniques allow less skilled individuals to conduct complex attacks, thereby diversifying and intensifying online threats.
As we navigate this evolving frontier, cybersecurity professionals must utilize AI-powered cybersecurity technologies to recognize and prepare for these emerging challenges in 2025. While seasoned cybercriminals have traditionally leveraged AI to bolster their attacks, this trend is now enabling even those with minimal technical expertise to engage in malicious activities. This shift mirrors the rise of “as-a-service” models in the cybercrime realm, making sophisticated tools accessible to a broader audience of potential attackers.
At its core, AI jailbreaking involves circumventing the built-in safeguards that AI developers implement to ensure ethical use and mitigate harmful outputs. These safeguards prevent AI models from generating inappropriate content, spreading misinformation, or engaging in harmful interactions. However, through jailbreaking, users can exploit these systems, unlocking capabilities that the original design intended to restrict. According to Microsoft, generative AI models are most susceptible to jailbreaking.
Here’s why.
Jailbreaking AI models often involve crafting specific prompts or employing methods that exploit the AI’s design weaknesses.
For instance, users may find ways to phrase questions that lead the AI to produce unintended outputs or ignore ethical constraints. As these techniques become more widely known, they empower a broader range of individuals to use AI in ways that can be detrimental or illegal.
AI jailbreaking can lead to a variety of significant risks that impact both safety and responsible usage. Here are some key examples:
AI Safety and Security Risks
- Unauthorized Data Access: Attackers may gain illicit access to sensitive data within AI systems, compromising privacy and confidentiality.
- Sensitive Data Exfiltration: Jailbroken AI models could be manipulated to extract and leak confidential information, posing a serious threat to organizations.
- Model Evasion: Cybercriminals might find ways to evade the protective measures built into AI models, allowing them to exploit vulnerabilities without detection.
- Generating Ransomware: With advanced capabilities, a compromised AI could potentially be used to create or facilitate ransomware attacks, increasing the threat of cyber extortion.
- Circumventing Compliance Systems: Jailbroken AI could be used to bypass internal policies or compliance protocols, leading to regulatory breaches and legal consequences.
Responsible AI Risks
- Content Violation: A jailbroken AI may produce harmful, offensive, or violent content that goes against established guidelines, undermining the responsible use of technology.
- Access to Dangerous Capabilities: Attackers could exploit the AI to generate actionable instructions for engaging in illegal or harmful activities.
- Subversion of Decision-Making Systems: Jailbroken models could be manipulated to influence critical systems, such as loan applications or hiring processes, resulting in biased or unethical outcomes.
- Public Misbehavior: Manipulating the AI to behave inappropriately could lead to sensational incidents that attract negative media attention, damaging reputations.
- Intellectual Property Infringement: Unauthorized use of AI may lead to violations of intellectual property rights, as attackers could exploit the model to generate content that infringes on copyrights or trademarks.
The rise of AI jailbreaking significantly expands the potential cyber threat landscape. It also opens new surface vulnerabilities against other advanced types of cyberattacks.
Unlike traditional cybercriminals, who often possess advanced technical skills, jailbreaking allows individuals with minimal knowledge to engage in malicious activities. This democratization of hacking tools could lead to a surge in cyber threats, as unskilled attackers leverage AI capabilities for phishing scams, misinformation campaigns, or even automated social engineering attacks.
The implications of AI jailbreaking extend beyond the immediate risks of misuse. As more individuals gain access to these capabilities, the potential for widespread disruption increases. For example, an attacker could use a jailbroken AI to generate realistic but fraudulent communications, leading to financial scams or reputational damage for organizations.
Moreover, the consequences may reach industries relying on AI for critical functions, such as healthcare or finance, where compromised models could lead to serious ethical and safety issues.
Countermeasures and Considerations against Advanced Types of Cyberattacks
To address the challenges posed by AI jailbreaking, developers and organizations must prioritize several countermeasures:
- Enhanced Security Features: Continuous improvement of AI models’ safety features can help mitigate risks. This includes regular updates to the AI’s underlying algorithms to better recognize and respond to jailbreaking attempts.
- User Education: Educating users about the ethical use of AI tools is crucial. Organizations should promote awareness of the potential consequences of jailbreaking and unauthorized use.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing monitoring systems to detect unusual AI behavior or outputs can aid in identifying potential jailbreaking attempts. Additionally, establishing clear reporting mechanisms for misuse can help organizations respond swiftly.
- Collaboration: Engaging in collaboration between AI developers, cybersecurity professionals, and regulatory bodies can foster a more secure AI ecosystem, addressing vulnerabilities and promoting best practices.
Recommendations for CISOs to Prevent AI Jailbreaking and Other Advanced Types of Cyberattacks
As the risks associated with AI jailbreaking become increasingly apparent, Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) play a crucial role in safeguarding AI systems. Here are several key strategies to mitigate the threat of AI jailbreaking:
1. Enhance AI Model Security
- Regular Audits and Updates: Conduct frequent security audits of AI models to identify and address vulnerabilities. Ensure that software updates and patches are applied promptly to protect against known exploits.
- Robust Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit who can interact with AI models. This includes using role-based access management and enforcing the principle of least privilege.
2. Develop Comprehensive Policies
- Establish Usage Guidelines: Create clear policies governing the acceptable use of AI technologies within the organization. Ensure all employees understand these guidelines and the importance of ethical AI usage.
- Compliance Frameworks: Align AI practices with compliance regulations and industry standards to foster responsible AI use and minimize risks related to data privacy and security.
3. Implement Advanced Monitoring Solutions
- Behavioral Monitoring: Deploy systems that monitor AI model behavior for signs of tampering or unusual activity. Anomalies can indicate potential jailbreaking attempts that require immediate investigation.
- Logging and Reporting: Maintain detailed logs of interactions with AI models. Establish reporting mechanisms for unusual requests or outputs, enabling rapid response to potential breaches.
4. Invest in Training and Awareness
- Employee Education: Provide regular training for employees on the risks of AI jailbreaking and the importance of security measures. Educate them about how to recognize suspicious behavior or content generated by AI.
- Cross-Department Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT, security, and AI development teams to ensure a unified approach to securing AI systems.
- Employ Technical Safeguards: Implement robust input validation mechanisms to detect and block malicious queries or commands aimed at manipulating AI outputs.
- Ethical Guardrails: Integrate ethical guardrails into AI models to prevent them from generating harmful content or instructions. This includes using fine-tuning techniques to enforce compliance with organizational policies.
5. Conduct Threat Modeling
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Regularly perform threat modeling to identify potential vulnerabilities within AI systems. Understanding attack vectors can help in devising strategies to fortify defenses.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for potential scenarios involving AI jailbreaking, outlining response strategies and incident management procedures.
6. Collaborate with Industry Peers
- Join Industry Groups: Engage with industry groups focused on AI security to share best practices, stay informed about emerging threats, and collaborate on solutions.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Participate in threat intelligence sharing initiatives to enhance understanding of AI-specific threats and trends in cybercrime.
CyberTechnology Insights conducts the Top Voice Program for the cybersec community. To participate, please write to us at news@intentamplify.com
#4 Remote Code Execution (RCE) attacks
An RCE attack occurs when an attacker gains the ability to execute malicious code on an organization’s systems or network. This capability can be exploited for numerous malicious activities, including deploying additional malware, exfiltrating sensitive data, or compromising system integrity. Attackers opt for chained methodologies to launch an RCE + LPE attack on the victims. It was recently reviewed at the Black Hat 2024 event, using examples of OpenVPN’s vulnerabilities.
Remote code execution (RCE) attacks typically exploit vulnerabilities found in web applications and network infrastructure. These vulnerabilities are flaws in software that enable an attacker to execute malicious code on a targeted system.
Various types of vulnerabilities can facilitate RCE, one of which is injection vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection or command injection, which arise from inadequate input sanitization.
When a user submits carefully crafted malicious input, the system may interpret part of this data as commands to execute, allowing the attacker to force the vulnerable system to run their code. Another example is insecure deserialization, where serialized data is packed for transmission. If the structure of this data is poorly defined, an attacker can manipulate the input. It could lead to misinterpretation during unpacking, resulting in an erroneous code execution.
Additionally, out-of-bounds write vulnerabilities occur when insecure data reads or writes allow an attacker to place data in memory areas that the application interprets as code or critical control information. File management issues can also be exploited; if an application permits users to upload files to a server, an attacker might upload a file containing malicious code, tricking the application into executing it.
Recommended: Proofpoint Signs Definitive Agreement to Acquire Normalyze
Essentially, RCE vulnerabilities provide a pathway for attackers to deploy malware in various ways. Consequently, RCE can be utilized to achieve similar objectives as traditional malware, such as deploying malicious software, conducting denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, or accessing sensitive information stored within the system.
#5 LLMjacking
LLMjacking is a term introduced by the Sysdig Threat Research Team (TRT) to describe the process by which attackers leverage stolen credentials to access a victim’s large language model (LLM). Essentially, it refers to the unauthorized hijacking of an LLM. Recently, we mentioned that LLMjacking attacks represent just the beginning of a much larger issue in an AI-driven cybersecurity landscape, where unprepared organizations could face losses of up to $100,000 per day. Despite significant efforts to promote awareness of cybersecurity frameworks and implement best practices, CISOs and CIOs often find themselves struggling against the escalating threats.
Organizations that utilize cloud-hosted LLMs face significant risks related to LLMjacking.
Attackers are drawn to LLMs for various motives, ranging from benign activities such as personal chats and image generation to more malicious intents like optimizing code or developing harmful tools. In some cases, these attacks can escalate to serious threats, including model poisoning or the theft of sensitive information.
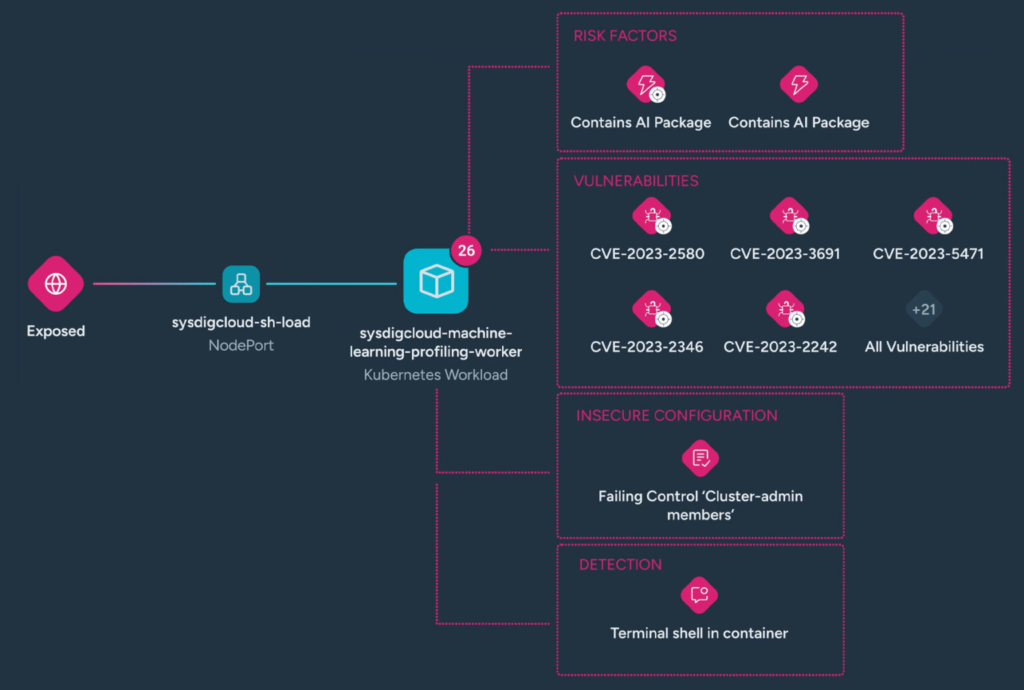
Sysdig’s AI workload security actively identifies and highlights vulnerabilities and misconfigurations across all AI-utilizing workloads, regardless of whether you are aware of them. This approach prioritizes protection and provides proactive defense against both known and unknown threats to your most sensitive data.
Conclusion
As we look ahead to 2025, the evolving landscape of cyber threats necessitates that CISOs remain vigilant and proactive in their defense strategies. The advanced types of cyberattacks outlined in this report underscore the need for robust security frameworks that can adapt to these emerging challenges. Industry leaders like Cisco, Sysdig, Fortinet, Rubrik, Proofpoint, and Cloudflare are continuously innovating to provide cutting-edge solutions that help organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. By leveraging these technologies and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, businesses can better protect their critical assets and sensitive information from increasingly sophisticated threats.
Top CyberTech Insights and News: Lumen and AWS Team Up to Enhance Generative AI Network Operations and Delivery
To share your insights, please write to us at news@intentamplify.com









